Affiliated Institute
- Gyeongju National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage
- Buyeo National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage
- Gaya National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage
- Naju National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage
- Jungwon National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage
- Seoul National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage
- Wanju National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage
- Cultural Heritage Conservation Science Center
Heritage Imaging Technology
Digital Restoration
Recently, diverse digital techniques based on 3D data, along with visual analysis, have been used to restore the estimated prototypes of relics, boosting their aesthetic and academic value, and greatly assisting with the identification of their production techniques. These data are used to review relics before conservation treatment and restoration.
Digital Restoration Process
1. Precision 3D Scanning
The target relic's characteristics are identified and a 3D scanner suitable for examining such characteristics is selected before scanning it closely and thoroughly. This process produces an abundance of data, which are used in the work of completing the forms of the relics.
 Precision 3D scanning
Precision 3D scanning
 Arrangement of acquired data
Arrangement of acquired data
2. Completion of 3D Forms
3D image data are combined and matched with each other to make a complete 3D image. An image is completed by dotting three or more identical points in the duplicated section when combining data.
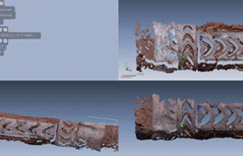 3-point combination
3-point combination
 Completion of 3D forms
Completion of 3D forms
3. Survey of Data
Before restoring images, using 2D photos and X-ray and CT images, not only the target relic's surface but also its interior should be observed, and various evidential historical data should be surveyed as reference data.
 Observation of a connected area and a sketch of a restored form
Observation of a connected area and a sketch of a restored form
 CT images - connection of central members and their characteristics
CT images - connection of central members and their characteristics
4. Dismantling by Member
The majority of relics are either damaged and lost or transformed in some way. As such, a part that is close to a prototype should be selected, and the relic should be dismantled by member before modeling each one.
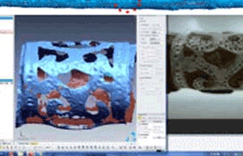 Dismantling by member
Dismantling by member
 Modeling of open-work decorative design
Modeling of open-work decorative design
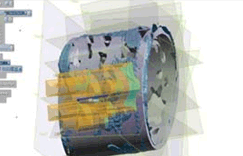
5. Correction of Transformed Forms
Based on modeled members, the transformed form is corrected.
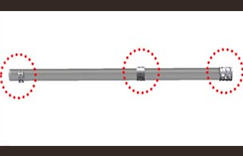 Difference between the corrected body and the existing member’s location
Difference between the corrected body and the existing member’s location
 Correction of detached band decoration- Attachment to the body
Correction of detached band decoration- Attachment to the body
6. Completion
Compare and examine the scanned data and the restored data and confirm the revised details before conducting the final examination
 Comparison with original data
Comparison with original data
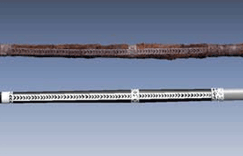 Final completion
Final completion
7. Videos
CT
Computer tomography (CT) is an inspection method by which the same x-ray equipment principle is used, radiation is injected from a high-pressure x-ray tube into the target relic, a 3D image isreconstructed, and its internal form, defects, and so on are analyzed.
View data
Non-Destructive Survey of Cultural Heritages Using CT
- Model: SEC X-EYE PCT
- Tube voltage: Max. 225kV
- Tube current: Max. 3mA
- Max. power: 300W
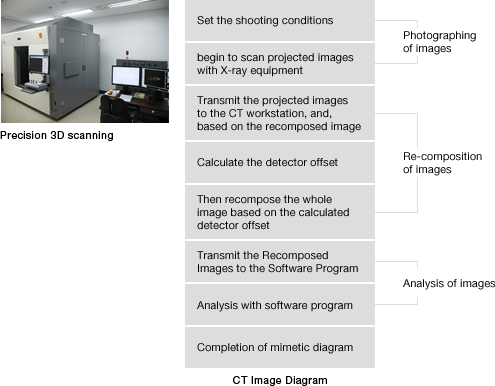
CT Image Diagram
presision 3D scanning
- Photographing of Images
- Set the shooting conditions
- begin ro scan projected images with X-ray equipment
- Re-composition of images
- Transmit the projected Images to the CT workstation, and, based on the recomposed image
- Calculate the detector offset
- Then recompose the whole image based on the calculated detector offset
- Analysis of images
- Transmit the Recomposed images to the Software Program
- Analysis with software program
- Completion of mimetic diagram
Characteristics of CT
- CT is conducted by shooting, recomposing, and analyzing images in that order.
- Shooting images: While the relic rotates by 360°, certain X-rays continue to be released to scan the images.
- Recomposing images: Transmit the scanned image files to the CT workstation to recompose them.
- Analyzing images: Use the CT-eye3D software and transform the recomposed images into 3D images to analyze information.
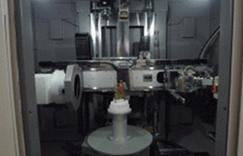 Internal CT structure
Internal CT structure
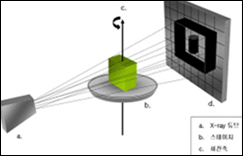 Principle of shooting
Principle of shooting
Examples of Non-destructive Survey Using CT
Goheung Gilt-bronze Decorative Shoes of Andong

Decorative shoes from the Andong ancient tomb in Goheung (Left: X-ray, center: photo, right: CT image)
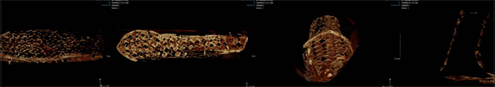
Diverse CT images of decorative shoes from the Ancient Andong Tomb
Bamboo tobacco pipe unearthed from Sungnyemun (Bronze)

Diverse CT images of the bamboo tobacco pipe unearthed from Sungnyemun
Fabrics collected from a sarira reliquary bronze bowl, Mireuksa Temple Site (Fabric)

Diverse CT images of fabrics from a bronze bowl, Mireuksa Temple Site
Treasure, Jade Furnace, Hyenchungsa Temple

Multiangle Filimg of the Jade Furnace, Hyeonchungsa Temple
Video
